In physics electrostatics is the study of charged particles that are not moving relative to each other. The equation that describes the forces between two such particles is Coulombs's Law . The law states that the magnitude of the electrostatic force of attraction or repulsion between two point charges is directly proportional to the product of the magnitudes of charges and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them. Coulomb's law can be seen in the equation below.
$$ F = k_e \frac{|q_1| |q_2|}{|r|^2} $$
Where \(k_e = \frac{1}{4\pi\epsilon_0}\). In this case \(\epsilon_0\) is the permittivity of free space. This is a number which dictates how easy it is to create an electric field in a vacuum. The permittivity (\(\epsilon\)) for materials is greater than in a vacuum and it is therefore harder to create an electric field.
Electric field lines are a representation of a vector field around all charged particles. The electric field can be defined for all space except at the location of point charges. It is defined as the electrostatic (Coulomb) Force divided by the charge of a test particle. This can be seen in equation below.
$$ E = \frac{F}{q} $$
Electric field lines are useful for understanding the formation of static charges. Field lines always point away from positive charges and towards negative charges. This means that positive charges cause positive divergence in the electric field.
Field lines can be represented in a number of ways. The most common ways are quiver plots and stream lines. Quiver plots are a grid of arrows which point in the direction of the field lines at those points. Streamplots are long continuous lines that start at a positive source and end at a negative source.
A positive charge is generally carried by protons in an atom. They can be exposed when electrons are ripped away from the atom leaving a positive nucleus behind. This happens in many scenarios where rubbing occurs or when electricity flows through an object. The electric field that is produced has a characteristic direction away from the positive charge.
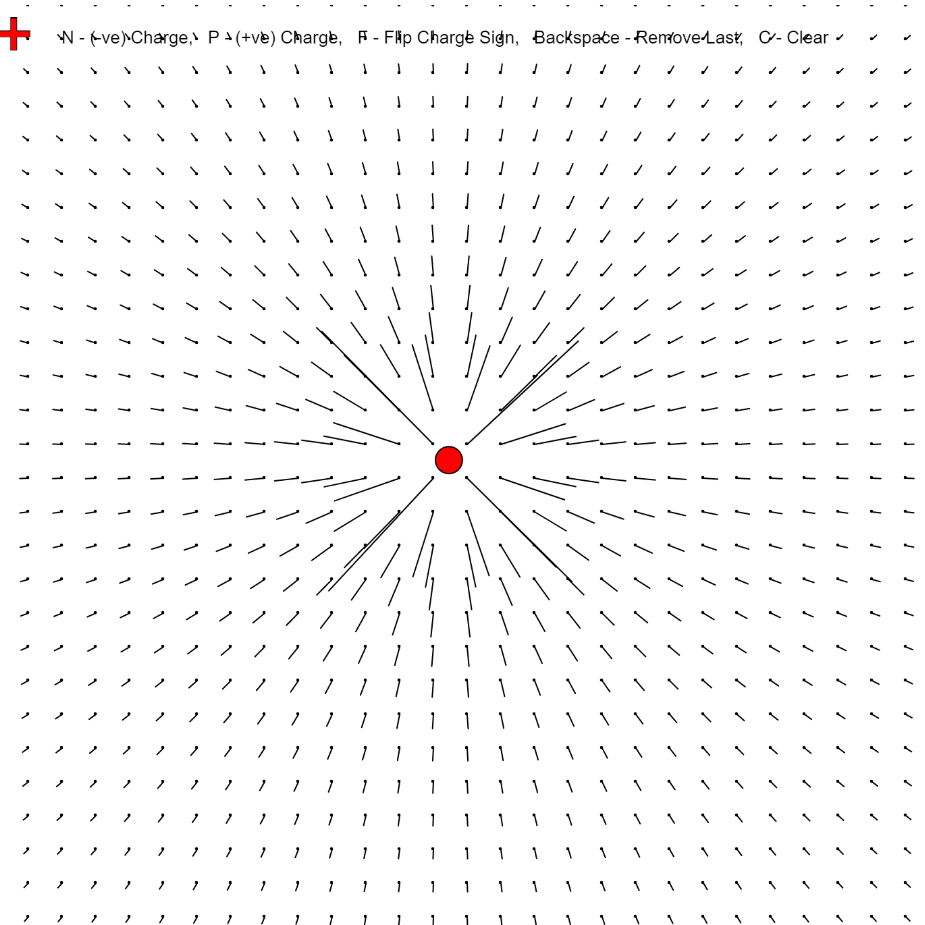
Image of a positive charge
A negative charge is generally carried by an electron. Electricity is generally a flow of electrons. There are however other sources of negative charge. Muons and Tauons are also negatively charged. Anti protons are also negatively charged. The electric field that is produced has a characteristic direction pointing towards the negatively charged particle.
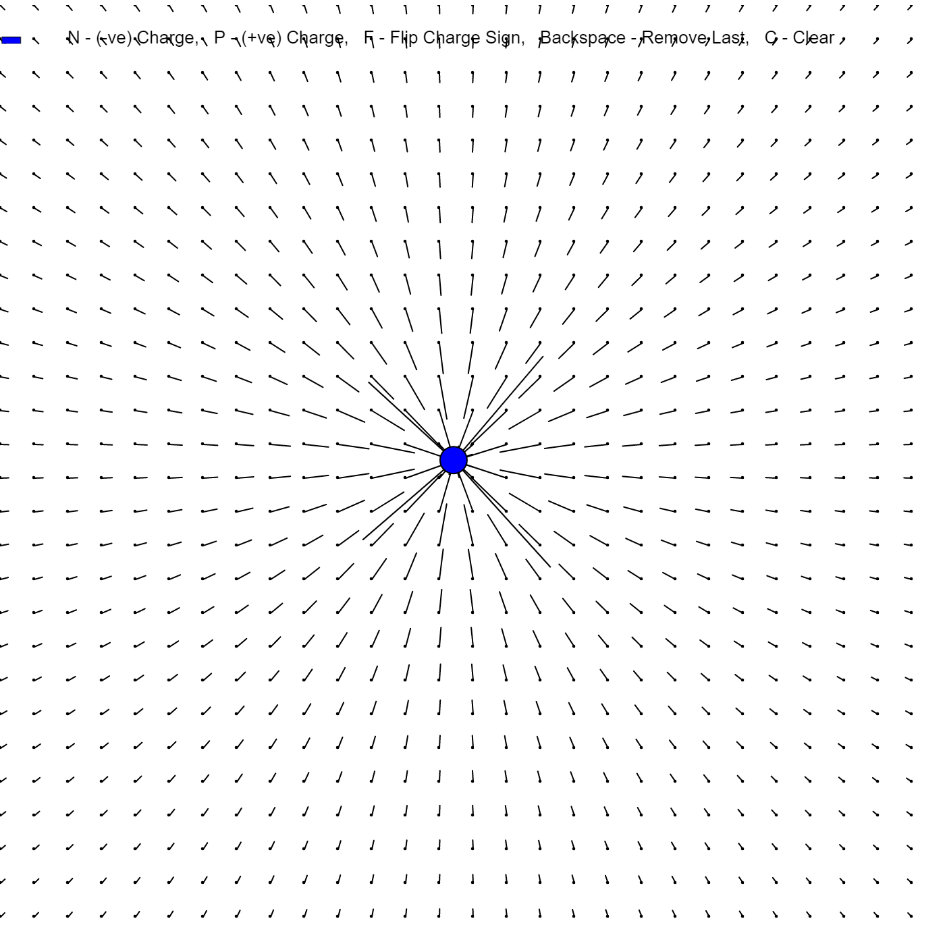
Image of a negative charge
An electric dipole is a positive and negative charge that are separated by infinitely small distance. In the real world this is not possible so it is modelled as two charges that are just very close together. The strength of the electric field as you get further and further away from the dipole drops as a rate of \(\frac{1}{r^3}\). This is much faster than either a positive or negative charge which have electric fields that drop off at a rate of \(\frac{1}{r^2}\) as is determined by Coulomb's law.

Image of a dipole